 |
| 1 |  | 
What is the difference between a virtual and a real image? State a method for demonstrating the presence of a real image. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
If the angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction for a light beam passing an interface, what can be said about the relative values of the indices of refraction and the speed of light in the first and second media? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
When a virtual image is formed by a mirror, is it in front of the mirror or behind it? What about a real image? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Light rays from the Sun, which is at an angle of 35° above the western horizon, strike the still surface of a pond. (a) What is the angle of incidence of the Sun's rays on the pond? (b) What is the angle of reflection of the rays that leave the pond surface? (c) In what direction and at what angle from the pond surface are the reflected rays traveling? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Sunlight strikes the surface of a lake at an angle of incidence of 30.0°. At what angle with respect to the normal would a fish see the Sun? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Calculate the critical angle for a sapphire surrounded by air. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Entering a darkened room, Gustav strikes a match in an attempt to see his surroundings. At once he sees what looks like another match about 4 m away from him. As it turns out, a mirror hangs on one wall of the room. How far is Gustav from the wall with the mirror? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
An object 2.00 cm high is placed 12.0 cm in front of a convex mirror with radius of curvature of 8.00 cm. Where is the image formed? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror with a 25.0-cm radius of curvature. A real image twice the size of the object is formed. At what distance is the object from the mirror? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
A point source of light is placed 10 cm in front of a concave mirror; the reflected rays are parallel. What is the radius of curvature of the mirror? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Laura is walking directly toward a plane mirror at a speed of 0.8 m/s relative to the mirror. At what speed is her image approaching the mirror? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
A ray of light is reflected from two mirrored surfaces as shown in Fig. 23.63. If the initial angle of incidence is 34°, what are the values of angles α and β? (The figure is not to scale.)
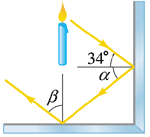 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Fig. 23.63::/sites/dl/free/0070524076/58006/23_063.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Fig. 23.63 (3.0K)</a>Fig. 23.63 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Fig. 23.63::/sites/dl/free/0070524076/58006/23_063.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Fig. 23.63 (3.0K)</a>Fig. 23.63 |
|  | |
|
|

