 |
1 |  | 
When testing for the equality of two population means, using α = 0.05 with n1 = 12 and n2 = 10, from independent samples, so long as the population variances can be assumed equal, the critical values for t are:: |
|  | A) | +2.704 and -2.704 |
|  | B) | +1.96 and -1.96 |
|  | C) | +2.086 and -2.086 |
|  | D) | +1.645 and -1.645 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
To test whether or not two population variances are equal, the appropriate distribution is: |
|  | A) | z distribution |
|  | B) | chi-square distribution |
|  | C) | F distribution |
|  | D) | t distribution with n1 + n2 - 2 degrees of freedom |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
An auto racing driver is given training and his timings on five different tracks are then measured. The times before and after training are given below. The differences are taken as before after. 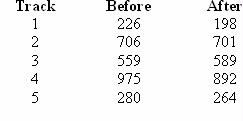 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> | | R-1 Ref 8-2 |
Compute the average difference, taking each difference as before after. |
|  | A) | 20.4 |
|  | B) | 102 |
|  | C) | 25.5 |
|  | D) | 32.4 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
An auto racing driver is given training and his timings on five different tracks are then measured. The times before and after training are given below. The differences are taken as before after. 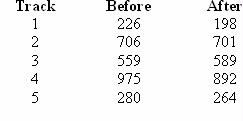 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> | | R-1 Ref 8-2 |
State the null hypothesis to test that the training was beneficial to this driver. |
|  | A) | H0: μD = 0 |
|  | B) | H0: μD ≥ 0 |
|  | C) | H0: μD > 0 |
|  | D) | H0:μD ≤ 0 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
An auto racing driver is given training and his timings on five different tracks are then measured. The times before and after training are given below. The differences are taken as before after. 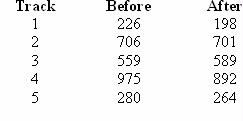 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/ref8_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> | | R-1 Ref 8-2 |
Was the training beneficial to this driver, at α = 0.01? |
|  | A) | Yes |
|  | B) | No |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
A major educational testing service is evaluating the performance of its new automated essay grading system. Student essays are scanned into a computer-recognizable format and then evaluated by the computer program. The software will not be moved into second-level testing unless there is compelling evidence that it finds more grammatical errors than human graders. A random sample of 100 essays evaluated by the software was compared to a different sample of 100 essays evaluated by humans. Results were as follows: 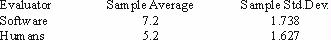 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>It is assumed that both software grading (population 1) and human grading (population 2) are normally distributed, with equal population variances. | | R-2 Ref 8-3 |
State the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether this software does pick out more errors. |
|  | A) | H0: μ1 - μ2 ≤ 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 > 0 |
|  | B) | H0: μ1 - μ2 = 0, H1: μ1 - μ2≠ 0 |
|  | C) | H0: μ1 - μ2 ≥ 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 < 0 |
|  | D) | H0: μ1 - μ2 > 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 ≤ 0 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
A major educational testing service is evaluating the performance of its new automated essay grading system. Student essays are scanned into a computer-recognizable format and then evaluated by the computer program. The software will not be moved into second-level testing unless there is compelling evidence that it finds more grammatical errors than human graders. A random sample of 100 essays evaluated by the software was compared to a different sample of 100 essays evaluated by humans. Results were as follows: 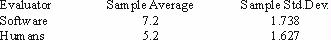 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>It is assumed that both software grading (population 1) and human grading (population 2) are normally distributed, with equal population variances. | | R-2 Ref 8-3 |
Find the critical points to test whether this software does find more errors, at α = 0.05. |
|  | A) | +1.96 |
|  | B) | +1.645 |
|  | C) | +1.282 |
|  | D) | +2.575 |
|  | E) | +2.33 |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
A major educational testing service is evaluating the performance of its new automated essay grading system. Student essays are scanned into a computer-recognizable format and then evaluated by the computer program. The software will not be moved into second-level testing unless there is compelling evidence that it finds more grammatical errors than human graders. A random sample of 100 essays evaluated by the software was compared to a different sample of 100 essays evaluated by humans. Results were as follows: 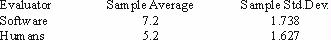 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>It is assumed that both software grading (population 1) and human grading (population 2) are normally distributed, with equal population variances. | | R-2 Ref 8-3 |
Compute the p-value for the test of this hypothesis. |
|  | A) | cannot compute from the information given |
|  | B) | about one-half |
|  | C) | very close to one |
|  | D) | very close to zero |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
A major educational testing service is evaluating the performance of its new automated essay grading system. Student essays are scanned into a computer-recognizable format and then evaluated by the computer program. The software will not be moved into second-level testing unless there is compelling evidence that it finds more grammatical errors than human graders. A random sample of 100 essays evaluated by the software was compared to a different sample of 100 essays evaluated by humans. Results were as follows: 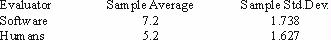 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070620164/235036/r8_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>It is assumed that both software grading (population 1) and human grading (population 2) are normally distributed, with equal population variances. | | R-2 Ref 8-3 |
Construct a 90% confidence interval for the average difference between the number of errors picked by the software and those found by human graders. |
|  | A) | 2 ± (1.96) (0.9552) |
|  | B) | 2 ± (2.33) (0.9552) |
|  | C) | 2 ± (1.645) (0.9552) |
|  | D) | 2 ± (1.28) (0.9552) |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
The average stock price of a particular company is $34 before a dividend is announced, for the last nine months, with a standard deviation of $2. After the dividend is announced, the average stock price is $37, with a standard deviation of $2.50 for the next nine months. State the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether this data provides evidence that a dividend release raises the stock price. Assume that population 1 is before the dividend release and population 2 is after. |
|  | A) | H0: μ1 - μ2 > 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 ≤ 0 |
|  | B) | H0: μ1 - μ2 = 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0 |
|  | C) | H0: μ1 - μ2 < 0, H1: μ1 - μ2 ≥ 0 |
|  | D) | H0: μ1 - μ2 ≥ 0, H1: μ1 - μ2< 0 |
|  | E) | H0: μ1 - μ2 ≤ 0, H1: μ1 - μ2> 0 |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
Using two independent samples, two population means are compared to determine if a difference exists. The number in the first sample is 15 and the number in the second sample is 12. How many degrees of freedom are associated with the critical t-value? |
|  | A) | 27 |
|  | B) | 26 |
|  | C) | 25 |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
Before a researcher can proceed with hypothesis tests involving a potential difference in population means, she hopes to first establish that the two population variances are equal. In a random sample of 18 observations from each of populations 1 and 2, she observes sample variances of, respectively, 33 and 47. Given α = 0.10, the critical lower and upper values for F are, respectively: |
|  | A) | FLOWER = 0.32, FUPPER = 3.10 |
|  | B) | FLOWER = 0.37, FUPPER = 2.67 |
|  | C) | FLOWER = 0.39, FUPPER = 2.60 |
|  | D) | FLOWER= 0.44, FUPPER = 2.27 |
|  | E) | FLOWER = 0.45, FUPPER = 2.22 |
 |

