 |
1 |  | 
What important conclusion was reached through the study of cathode rays? |
|  | A) | Cathode rays were proved to be light rays indicating that atoms were indeed indivisible. |
|  | B) | Cathode rays were shown to be positively charged particles indicating that atoms contained electric charge. |
|  | C) | Cathode rays were shown to be negatively charged particles. |
|  | D) | The ratio of the charge to mass ratio of particles making up cathode rays was constant, indicating they were fundamental particles found in all matter. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
How did Thompson establish whether or not cathode rays were light? |
|  | A) | He could tell by visual observation. |
|  | B) | Thompson knew light rays would be deflected by electric or magnetic fields and he determined experimentally that they were not deflected. |
|  | C) | Thompson knew light rays would not be deflected by electric or magnetic fields and he determined experimentally that the rays were deflected. |
|  | D) | He determined experimentally if the rays would be deflected by gravity; light rays would not be deflected. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
After the existence of the electron was established by Thompson, Millikan's contribution added what additional information to atomic theory? Millikan |
|  | A) | proved electrons had a variable charge. |
|  | B) | measured the fixed negative charge of the electron. |
|  | C) | proposed the existence of protons. |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
After the mass and charge of the electron was known, the next breakthrough in the development of atomic theory was made by Rutherford. What important result was established by Rutherford? |
|  | A) | The atom was of uniform substance containing electrons arranged like raisins in plum pudding. |
|  | B) | Rather than being spread out, electrons occupied one half of an atom and the positive charges occupied the other half. |
|  | C) | Electrons disappeared inside an atom. They only existed outside. |
|  | D) | All positive charge in an atom was concentrated at a tiny part of the center. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
What new concept did Bohr adapt and use to formulate his model of the atom? |
|  | A) | The quantum concept developed by Planck. |
|  | B) | Electromagnetic theory developed by Maxwell. |
|  | C) | Photoelectric theory developed by Thompson. |
|  | D) | Neutron theory developed by Chadwick. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
What basis did Bohr have for allowing only specific orbits for electrons in his model of the atom? |
|  | A) | Specific orbits were proven experimentally. |
|  | B) | Bohr assumed only specific orbits were allowed. |
|  | C) | Allowed orbits were predicted from electromagnetic theory. |
|  | D) | It was the general consensus of the scientific community. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
The idea that electrons have wave properties |
|  | A) | was never proved and is now discounted. |
|  | B) | was only proved theoretically. |
|  | C) | was proved experimentally. |
|  | D) | is true, but of no consequence. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Quantum mechanics considers electron energy levels in an atom and identifies those levels with four quantum numbers. The first, the principal quantum number considers what property of an electron? |
|  | A) | energy sublevel |
|  | B) | distance from the nucleus |
|  | C) | orientation in space |
|  | D) | direction of spin |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
The second, or angular momentum quantum number, considers what property? |
|  | A) | energy sublevel |
|  | B) | distance from the nucleus |
|  | C) | orientation in space |
|  | D) | direction of spin |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
The third quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, considers what property? |
|  | A) | energy sublevel |
|  | B) | distance from the nucleus |
|  | C) | orientation in space |
|  | D) | direction of spin |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
The fourth quantum number, the spin quantum number, considerers what property? |
|  | A) | energy sublevel |
|  | B) | distance from the nucleus |
|  | C) | orientation in space |
|  | D) | direction of spin |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
The distribution of electrons in an atom is specified by the quantum numbers of each electron. What important principle governs the assignment of quantum numbers to electrons in an atom? |
|  | A) | The Schrodinger inclusion principle states that quantum numbers must be assigned to all available electrons. |
|  | B) | The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that the exact position and momentum of an electron cannot be determined at the same time. |
|  | C) | The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers. |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
Isotopes are atoms of an element with identical |
|  | A) | masses but different abundances. |
|  | B) | masses but different chemical properties. |
|  | C) | chemical properties but different masses. |
|  | D) | abundances but different masses. |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
The weighted average of the masses of stable isotopes of an element as they occur in nature is called the |
|  | A) | average atomic mass. |
|  | B) | atomic weight. |
|  | C) | atomic mass. |
|  | D) | atomic mass unit. |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
The isotope used as a standard for measuring atomic masses is |
|  | A) | carbon-12. |
|  | B) | carbon-14. |
|  | C) | hydrogen-1. |
|  | D) | oxygen-16. |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
The mass of the carbon-12 isotope is |
|  | A) | 12.00 grams. |
|  | B) | 1.00 grams. |
|  | C) | 1.00 units. |
|  | D) | 12.00 units. |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
The atomic number identifies the total number of |
|  | A) | particles in an atom. |
|  | B) | protons in the nucleus. |
|  | C) | neutrons in the nucleus. |
|  | D) | particles in the nucleus. |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
The nucleus of element 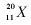 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072467002/80549/chap08image.jpg','popWin', 'width=81,height=95,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072467002/80549/chap08image.jpg','popWin', 'width=81,height=95,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>
has |
|  | A) | 9 neutrons. |
|  | B) | 20 protons. |
|  | C) | 11 neutrons. |
|  | D) | 20 neutrons. |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
Select the correct statement about the elements in the periodic table. Each |
|  | A) | family begins with a single electron in a new outer energy level. |
|  | B) | period has elements with similar properties. |
|  | C) | period ends with the filling of an orbital in an outer energy level. |
|  | D) | family has atoms with equal number of filled energy levels. |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
The chemical properties of an element are determined by |
|  | A) | the period to which it belongs. |
|  | B) | number of filled energy levels. |
|  | C) | number of electrons in its outer energy levels. |
|  | D) | the total number of electrons. |
 |
 |
21 |  | 
An element in the family VIA has |
|  | A) | six electrons in its atom. |
|  | B) | six occupied energy levels in its atom. |
|  | C) | six electrons in its outer energy level. |
|  | D) | five other elements in its family. |
 |
 |
22 |  | 
Select the correct statement about elements in the periodic table. |
|  | A) | Members of the A-group family are called transition elements. |
|  | B) | Members of the B-group family are called representative elements. |
|  | C) | Alkali metals are members of the group I |
|  | D) | Alkaline earth metals are members of the group I |
 |
 |
23 |  | 
Select the incorrect statement about halogens. |
|  | A) | Halogens are nonmetals. |
|  | B) | Halogens react with metals to form salts. |
|  | C) | Halogens lie in group VII |
|  | D) | Iodine is not a halogen. |
 |
 |
24 |  | 
Which of the following is indicated by the number of dots in the electron dot notation. The number of electrons |
|  | A) | in the atom. |
|  | B) | in the outer energy level. |
|  | C) | missing from the outer energy level. |
|  | D) | in the inner energy levels. |
 |
 |
25 |  | 
Select the term used to describe an atom that has acquired an unbalanced electron charge. |
|  | A) | noble |
|  | B) | semiconductor |
|  | C) | allotropic |
|  | D) | ion |
 |

