(See related pages)
Have you ever received a C grade on a paper and thought you deserved better? In 1965 Fred Smith did. His term paper for an economics class proposed a revolutionary air freight delivery method that revolved around a “hub and spokes” system. The hub would be located in a middle-America location (Memphis was eventually chosen) with spokes radiating out to cities across the country. A package from Los Angeles, destined for New York, would be flown in on the Los Angeles spoke in a few hours to the hub location in Memphis. There it would be sorted and routed out on the return flight of the plane that had just brought in shipments from New York, arriving before dawn. Los Angeles to New York overnight!
Fred Smith had so much confidence in his idea that in 1971 he created a company called Federal Express. On April 17, 1973, when operations officially began, the company served 25 cities and delivered 186 packages. The company struggled at first, and it wasn’t until three years later that it reported its first profit of $3.6 million. A quarter of a century later, Federal Express Corporation’s annual profit exceeded $580 million and annual revenue topped $19 billion. Average package volume reached approximately 3.2 million daily worldwide.1 FedEx Corporation Many factors contributed to the success of Federal Express. The company’s founder was visionary in terms of his package delivery system. The hub and spokes concept is now used throughout the air freight industry. A key factor contributing to the growth and success of Federal Express was its access to external capital (resources). At various times in the company’s brief history, the ability to raise external capital from investors and creditors was critical to its phenomenal growth. For example, several bank loans provided financing in the early years, and in 1978, an initial public offering of the company’s stock provided over $17 million in equity financing. Investors and creditors use many different kinds of information before supplying capital to business enterprises like Federal Express. The information is used to assess the future risk and return of their potential investments in the enterprise.2 For example, information about the enterprise’s products and its management is of vital importance to this assessment. In addition, various kinds of financial information are extremely important to investors and creditors.
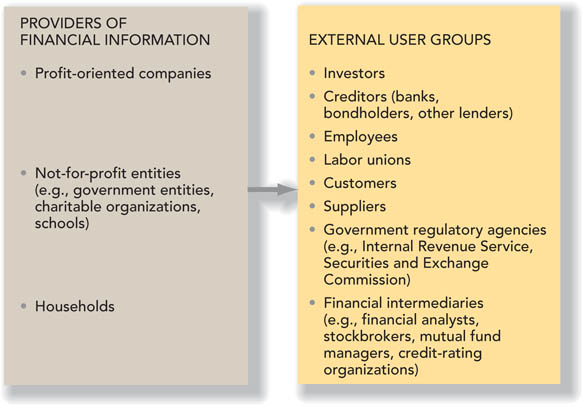
lLO1 You might think of accounting as a special “language” used to communicate financial information about a business to those who wish to use the information to make decisions.Financial accountingprovides relevant financial information to various external users., in particular, is concerned with providing relevant financial information to various external users. The chart in Graphic 1-1 illustrates a number of financial information supplier groups as well as several external user groups. Of these groups, the primary focus of financial accounting is on the financial information provided by profit-oriented companies to their present and potential investors and creditors. The reason for this focus is discussed in a later section of this chapter. One external user group, often referred to as financial intermediaries, includes financial analysts, stockbrokers, mutual fund managers, and credit rating organizations. These users provide advice to investors and creditors and/or make investment-credit decisions on their behalf. The collapse of Enron Corporation in 2001 and other high profile accounting failures made immensely clear the importance of reporting reliable financial information.
On the other hand, managerial accountingdeals with the concepts and methods used to provide information to an organization's internal users (i.e., its managers). deals with the concepts and methods used to provide information to an organization’s internal users, that is, its managers. You study managerial accounting elsewhere in your curriculum. The primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial statements and related disclosure notes. The financial statements most frequently provided are (1) the balance sheet or statement of financial position, (2) the income statement or statement of operations, (3) the statement of cash flows, and (4) the statement of shareholders’ equity. As you progress through this text, you will review and expand your knowledge of the information in these financial statements, the way the elements in these statements are measured, and the concepts underlying these measurements and related disclosures. We use the term financial reportingprocess of providing financial statement information to external users. to refer to the process of providing this information to external users. Keep in mind, though, that external users receive important financial information in a variety of other formats as well, including news releases and management forecasts, prospectuses, reports filed with regulatory agencies, and the president’s letter.
Appendix B located at the back of this text contains recent financial statements, including related disclosure notes, for FedEx Corporation, now the parent company of Federal Express. We occasionally refer to the FedEx financial statements to illustrate certain points. You also can refer to these statements as new topics are introduced in later chapters. FedEx Corporation 1 Vance Trimble, Overnight Success (New York: Crown Publishers, Inc., 1993). 2 Risk refers to the variability of possible outcomes from an investment. Return is the amount received over and above the investment and usually is expressed as a percentage. |