 |
1 |  | 
For the overall hypothetical reaction A + 5B ----> 4C the rate of appearance of C, given by D[C]/Dt, may also be expressed as: |
|  | A) | 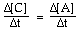 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1a.gif','popWin', 'width=96,height=45,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1a.gif','popWin', 'width=96,height=45,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 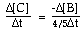 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1b.gif','popWin', 'width=99,height=46,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1b.gif','popWin', 'width=99,height=46,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 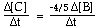 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1c.gif','popWin', 'width=115,height=44,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1c.gif','popWin', 'width=115,height=44,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 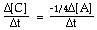 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1d.gif','popWin', 'width=113,height=46,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0073656011/17481/ch13quizaq1d.gif','popWin', 'width=113,height=46,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
A certain first order reaction, A ----> B, when performed at 25 oC, is 46% complete after 68 min. What is the rate constant of this reaction? |
|  | A) | 9.06 x 10-3 min-1 |
|  | B) | 1.14 x 10-2 min-1 |
|  | C) | 31 min-1 |
|  | D) | -1.14 x 10-2 min-1 |
|  | E) | 51 min-1 |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Determine the rate constant for a first order reaction that has a half-life of 26.7 min. |
|  | A) | 18.5 min-1 |
|  | B) | 38.5 min-1 |
|  | C) | 9.25 min-1 |
|  | D) | 19.3 min-1 |
|  | E) | 0.026 min-1 |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
A second order reaction has a rate constant of 1.0 x 10-3 Lmol-1 s-1. If the initial reactant concentration is 0.200 M, how long will it take for the concentration to become 0.0250 M? |
|  | A) | 4.0 x 104 s |
|  | B) | 3.5 x 104 min |
|  | C) | 3.5 x 104 s |
|  | D) | 8000 s |
|  | E) | 3.5 x 10-2 s |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
Determine the half-life of a second order reaction with k = 1.0 x 10-3 Lmol-1s-1 if the initial reactant concentration is 0.200 M. |
|  | A) | 200 s |
|  | B) | 5000 s |
|  | C) | 0.005 s |
|  | D) | 2 x 10-4 s |
|  | E) | None of the above. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
If the rate of the reaction PCl5 ----> PCl3 + Cl2 is increased by a factor of four when the PCl5 concentration doubles, the rate law for this reaction must be |
|  | A) | dependent on the PCl3 and Cl2 concentrations |
|  | B) | first order with respect to PCl5 |
|  | C) | second order with respect to PCl5 |
|  | D) | fourth order with respect to PCl5 |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
If a reaction has a rate constant of 3.7 x 10-3 s-1 at 25 oC, and an activation energy of 43.6 kJ/mol, what will be the rate constant for this reaction at 75 oC? |
|  | A) | A one-step mechanism involving a transition state that contains two hydroxide ions "attached" to the carbon atom of CH3Cl |
|  | B) | A one-step mechanism involving a transition state that has a carbon partially bonded to both chlorine and oxygen |
|  | C) | A two-step mechanism in which the chlorine leaves CH3Cl in a slow step, followed by rapid attack of the intermediate by the hydroxide ion |
|  | D) | A two-step mechanism in which the chlorine leaves CH3Cl in a rapid step, followed by the slow attack of the intermediate by the hydroxide ion |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by |
|  | A) | increasing the enthalpy of the reaction |
|  | B) | lowering the activation energy of the reaction |
|  | C) | increasing the activation energy of the reaction |
|  | D) | decreasing the enthalpy of the reaction |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
The reaction H2(g) + I2(g) ----> 2 HI(g) is exothermic and has the following rate law at 298K: rate = [H2][I2]. Addition of a catalyst would |
|  | A) | increase the rate of the forward reaction |
|  | B) | increase the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions |
|  | C) | increase the rate of the reverse reaction |
|  | D) | cause no increase or decrease in the rate of the reaction |
|  | E) | None of the above |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
Which of the following is a likely mechanism for the reaction CH3Cl + OH- ----> CH3OH + Cl-, which is first order with respect to each of the reactants. |
|  | A) | A one-step mechanism involving a transition state that contains two hydroxide ions "attached" to the carbon atom of CH3Cl |
|  | B) | A one-step mechanism involving a transition state that has a carbon partially bonded to both chlorine and oxygen |
|  | C) | A two-step mechanism in which the chlorine leaves CH3Cl in a slow step, followed by rapid attack of the intermediate by the hydroxide ion |
|  | D) | A two-step mechanism in which the chlorine leaves CH3Cl in a rapid step, followed by the slow attack of the intermediate by the hydroxide ion |
 |



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education

 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education