 |
| 1.
|  | 
The EU25 is an example of a(n) |
|  | A) | free-trade area |
|  | B) | customs union |
|  | C) | common market |
|  | D) | monetary union |
|  | E) | economic union |
|
|
 |
| 2.
|  | 
The Stability and Growth Pact further strengthened the need for labour mobility within and across the EU15 due to: |
|  | A) | poor capital mobility |
|  | B) | perfect capital mobility |
|  | C) | large fiscal transfers |
|  | D) | small fiscal transfers |
|  | E) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 3.
|  | 
Trade Distortion is: |
|  | A) | the consequence of increasing a country's level of tariffs |
|  | B) | the consequence of reducing tariifs between countries in a free trade area while leaving tariffs against non-member countries unchanged |
|  | C) | an inevitable consequence of trade creation through tariff reduction |
|  | D) | greater than trade creation in the history of the EU |
|  | E) | eliminated if a free trade area becomes a monetary union |
|
|
 |
| 4.
|  | 
The EU25 is an example of a(n) |
|  | A) | free-trade area |
|  | B) | customs union |
|  | C) | common market |
|  | D) | monetary union |
|  | E) | economic union |
|
|
 |
| 5.
|  | 
EU rules limit the ability of members to impose regulation because |
|  | A) | regulation can be used to distort trade within the EU |
|  | B) | regulation is a power that has largely been transferred to the EU Commission |
|  | C) | it has been shown that regulation has been subject to regulatory failure |
|  | D) | Governments have used regulation as a means to redistribute income |
|  | E) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 6.
|  | 
The Cassis de Dijon case |
|  | A) | is an example of the EU imposing similar product quality rules across the EU |
|  | B) | is an example of the EU preventing countries from using regulation to distort trade |
|  | C) | shows that the EU places a high value on consumer protection |
|  | D) | had little real effect on the development of trade and integration within the EU |
|  | E) | was most important in terms of its impact on trade relations between EU states and non-members |
|
|
 |
| 7.
|  | 
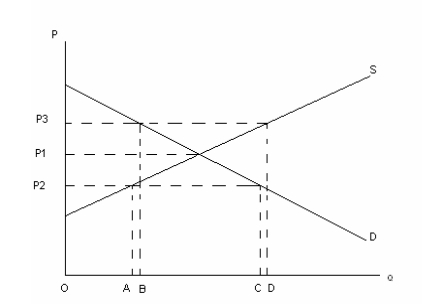 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Diagram 1::/sites/dl/free/0077108310/329312/mcdowellimage1.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Diagram 1 (23.0K)</a>Diagram 1
Consider the above diagram which represents the supply and demand for widgets in a country called Freelandia. When there is no international trade, the output and price of widgets are given by the intersection of supply and demand with a price of P1. That is, all domestic demand is met by domestic supply. Now consider that international trade is possible and that world prices may be higher or lower than domestic prices.
If Freelandia trades with the rest of the world and the world price is P3, then Freelandia: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Diagram 1::/sites/dl/free/0077108310/329312/mcdowellimage1.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Diagram 1 (23.0K)</a>Diagram 1
Consider the above diagram which represents the supply and demand for widgets in a country called Freelandia. When there is no international trade, the output and price of widgets are given by the intersection of supply and demand with a price of P1. That is, all domestic demand is met by domestic supply. Now consider that international trade is possible and that world prices may be higher or lower than domestic prices.
If Freelandia trades with the rest of the world and the world price is P3, then Freelandia: |
|  | A) | becomes a net importer |
|  | B) | becomes a net exporter |
|  | C) | does not import or export |
|  | D) | produces less widgets |
|  | E) | produces the same amount of widgets |
|
|
 |
| 8.
|  | 
Consider the above diagram again, which represents the supply and demand for widgets in a country called Freelandia.
Consider the case where prices move to P2, then Freelandia: |
|  | A) | produces more widgets |
|  | B) | becomes a net exporter |
|  | C) | does not import or export |
|  | D) | produces the same amount of widgets |
|  | E) | becomes a net importer |
|
|
 |
| 9.
|  | 
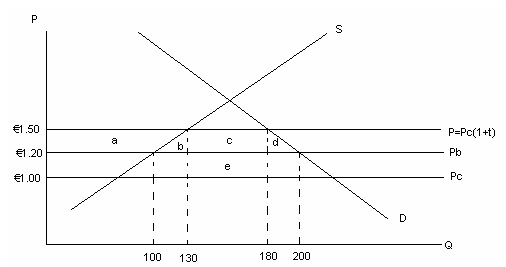 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Diagram 2::/sites/dl/free/0077108310/329312/mcdowellimage2.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Diagram 2 (30.0K)</a>Diagram 2
Study the above diagram. Consider the case where Freelandia has no trade agreements and has a 50% tariff on the imports of widgets. Freelandia trades with two countries B and C, whose prices are represented by the lines Pb and Pc. Freelandia imports from country C as the tariff inclusive price is €1.50. It does not import from country B as the tariff inclusive price of imports from B is €1.80 (not shown). Suppose that Freelandia enters into a customs union with country B, but maintains its tariff on imports of widgets from C.
Under these conditions, the increase in consumer surplus in Freelandia is represented by an area: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Diagram 2::/sites/dl/free/0077108310/329312/mcdowellimage2.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Diagram 2 (30.0K)</a>Diagram 2
Study the above diagram. Consider the case where Freelandia has no trade agreements and has a 50% tariff on the imports of widgets. Freelandia trades with two countries B and C, whose prices are represented by the lines Pb and Pc. Freelandia imports from country C as the tariff inclusive price is €1.50. It does not import from country B as the tariff inclusive price of imports from B is €1.80 (not shown). Suppose that Freelandia enters into a customs union with country B, but maintains its tariff on imports of widgets from C.
Under these conditions, the increase in consumer surplus in Freelandia is represented by an area: |
|  | A) | a+b+c+d |
|  | B) | a+b |
|  | C) | c |
|  | D) | b+d |
|  | E) | e |
|
|
 |
| 10.
|  | 
Consider the above diagram again. The area ____ reflects the part of the government revenue given up after integration that is transferred to the consumers through a reduction in prices. |
|  | A) | a |
|  | B) | b |
|  | C) | c |
|  | D) | d |
|  | E) | e |
|
|

