|  Behavioral Statistics in Action, 3/e Mark W. Vernoy,
Palomar College
Diana J. Kyle,
Fullerton College
Chi-Square And Other Nonparametric Statistics
Glossary
| Chi-square | 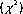 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/chap15g_1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> is a statistical technique for nominal data comparing the observed frequencies in different categories with the frequencies expected from a theory or hypothesis. The test requires that the observations are independent, randomly sampled, nominal data, and that not less than 5 expected frequencies are in a cell. <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/chap15g_1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> is a statistical technique for nominal data comparing the observed frequencies in different categories with the frequencies expected from a theory or hypothesis. The test requires that the observations are independent, randomly sampled, nominal data, and that not less than 5 expected frequencies are in a cell.
|  |  |  | | Kruskal-Wallis test | is a nonparametric test that analyzes studies with more than two independent samples. It is the nonparametric counterpart of the one-way analysis of variance.
|  |  |  | | Mann-Whitney U | is a nonparametric test that analyzes two independent samples. It is the nonparametric counterpart of the independent groups t test.
|  |  |  | | Nonparametric statistics | do not compare population parameters and make fewer assumptions than parametric statistics. The major advantage of most nonparametric statistics is that they work well with data that are ranked or skewed, as well as with small samples. The disadvantage is that, on average, nonparametric statistics are less powerful.
|  |  |  | | Parametric statistics | are stated in terms of and make assumptions about population parameters (the characteristic elements of a population under study, such as the population mean and standard deviation). For example, the hypothesis for the t test and the analysis of variance are stated terms of the population mean and we can assume that the variances of the populations being compared are equal and the scores are normally distributed.
|  |  |  | | Sign the ranks | is a process whereby each rank is assigned to a category based on the arithmetic sign of the difference score for that rank. If the difference score is negative, the rank is assigned to the minus category; if the difference is positive, the rank is assigned to the plus category.
|  |  |  | | Wilcoxon T | is a nonparametric test that determines if there is a significant difference between two correlated samples. The major requirements of the test are (1) that the sample is correlated and (2) it is possible to rank the differences between the samples. The Wilcoxon T is the nonparametric counterpart of the correlated samples t test.
|
|



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education